Dependent Services Configuration
Cafe Variome V3 relies on multiple services to function correctly, including databases, storage systems, and identity providers.
MongoDB
MongoDB is a schemaless NoSQL database used by Cafe Variome V3 to store both operational and discoverable data.
Official document can be found here. For Ubuntu, it can be installed via a custom source:
The minimal setup for docker would be:
How to install as a tarball.
MongoDB supports authentication. It is recommended to enable authentication for production use. The corresponding configuration section of CV3 is:
If authentication is not enabled, the username and password can be left empty or set to any value.
Redis
Redis is a high speed in-memory cache storage that Cafe Variome V3 uses as a message broker and inter-process cache.
Redis comes with most distributions' package managers. For Ubuntu, it can be installed via:
The minimal setup for docker would be:
How to install as a tarball.
Redis does not use traditional username/password authentication but instead relies on an ACL system. Currently, CV3 does not support this authentication method and only works with Redis without authentication.
Redis may also be configured as a cluster. When using a redis cluster, set the cluster option in CV3 configuration to true.
Keycloak
Keycloak is an open source OIDC identity provider that Cafe Variome V3 uses to authenticate users. CV3 integrates with Keycloak deeply, not only by using the OIDC protocol, but also uses its REST API to manage users, tokens and clients. It currently cannot use a different OIDC server.
Using Keycloak docker
It's recommended to use Keycloak with docker. Otherwise, the server should be specifically hardened, and Keycloak should be run as a service to ensure availability and security.
The minimal setup for docker would be:
This set up is for a dev server. For production use, you need to use `start` instead of `start-dev`, and may need to configure Java keystore for SSL, as well as other security settings.
How to install as a tarball.
Cafe Variome V3 requires a service account with sufficient privileges to manage users and handle token operations. The necessary roles, which may be assigned to different clients, include:
view-users
manage-users (optional if need to create users)
read-token
manage-account
manage-account-links
view-groups
view-applications
delete-account
view-profile
If you wish to use the Nexus mode (which manages multiple CV2 instances), you will also need to assign the following roles:
create-client
manage-clients
view-clients
For federated authentication, a client role must be created with audience mappers for all clients that need to support this feature. This role should then be set as a default client role for those clients. By doing so, their access tokens will automatically include the necessary audiences. An example is:
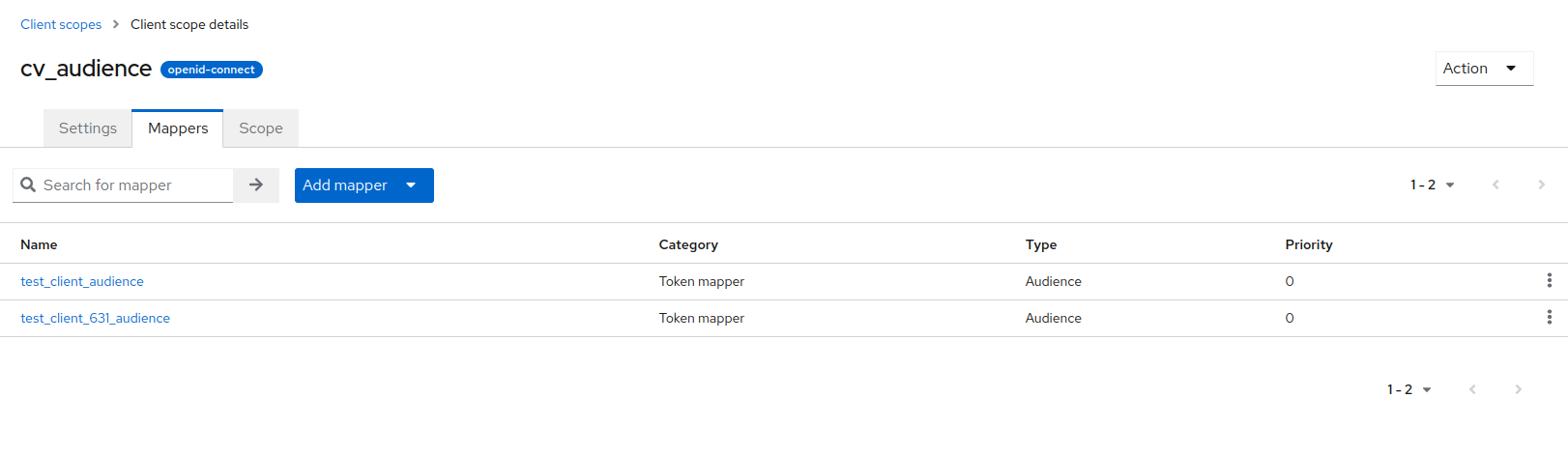
The two clients are the ones assumed that will be used for federated authentication.
To set up the credentials in KeyCloak 21+, follow the steps below:
Create credentials in KeyCloak 21+
To set up the credentials in KeyCloak 21+, follow the steps below:
Log in to KeyCloak as an administrator. The administrator account can be the global admin in master realm, or any admin account with the
realm-managementrole in the realm you wish to use.Go to the realm you wish to use, and go to the
Clientspage.Click the
Create clientbutton to create a new client.Set the client type to
Service account, and the client ID, client name, and description to something you wish to use. ClickSaveto save the client.In Capability config, enable
Client authentication,Standard flowandService accounts roles. For security purpose, it's recommended to disableDirect access grantsand any other flow you do not use. ClickNextto go to login settings.In the Login settings, configure all URLs to match the intended hosting location of the service. Assuming the domain hosting the service is
https://cv3.cafevariome.org, the valid redirect URLs would be:https://cv3.cafevariome.org/callback.htmlhttps://cv3.cafevariome.org/callback-silent.htmlhttps://cv3.cafevariome.org/discover/callback.htmlhttps://cv3.cafevariome.org/discover/callback-silent.htmlhttps://cv3.cafevariome.org/meta-discover/callback.htmlhttps://cv3.cafevariome.org/meta-discover/callback-silent.html
A wildcard can be used to simplify URL management. However, due to the frontend code structure, only these specified URLs will be valid for redirection. Click
Saveto save the settings.Go to the configuration page for the newly created client, and select
Service accounts rolestab. ClickAssign roleto assign the aforementioned roles to the client.Go to the
Client Scopespage and create a new client scope, following instructions in the image above. Assign this role to the client as a default client role.Fine tune other settings for this client.
At this point, the client should be ready to use CV3.
Vault
Vault is a powerful secret management tool that focuses on security. It's a web service that stores secrets, such as passwords, encryption keys, and other sensitive data. It stores everything in an encrypted form, and supports encryption / decryption as a service.
On some distributions, Vault can be installed via package manager. For Ubuntu, it can be installed like this:
Hashicorp provides an official docker image for Vault. It can be used like:
The `IPC_LOCK` capability is mandatory for vault to work. The configuration of the vault can be supplied as an environment variable, or as a file. The above example uses environment variable.
Vault is a self-contained binary that contains both the web service and a CLI tool to interact with the service. Refer to the official website to download the binary.
Vault requires unsealing each time it restarts. While this process can be automated using methods like AWS KMS or Azure Key Vault (which is recommended for production), we'll use a simple manual unseal process here for demonstration purposes.
Configure Hashicorp Vault
To configure Hashicorp Vault for use with Cafe Variome, follow the steps below:
Install the vault, configure it, and start the server. It's recommended to use high availability set up or auto unseal to ensure the availability of the vault server. Initialize and unseal the vault. For details on these steps, refer to official vault documents
Enable kv store and transit engine for CV3, if not done so already. Run the following command (note that it's kv-v2, not kv):
# Enable kv store vault secrets enable -path=kv kv-v2 # Enable transit engine vault secrets enable -path=transit transitCreate a policy that allows the CV3 to access necessary paths. CV3 needs full permission on the designated kv engine path, as well as permission to list and remove metadata for the same path (to check the key status and to completely remove a key). It also needs full access to the transit engine. A sample policy would be (assume the kv engine is mounted at
kv, and the designated path iscv3, while the transit engine is mounted attransit_cv3):path "kv/data/cv3" { capabilities = ["create", "update", "read", "delete", "list"] } path "kv/data/cv3/*" { capabilities = ["create", "update", "read", "delete", "list"] } path "kv/metadata/cv3" { capabilities = ["list", "delete"] } path "kv/metadata/cv3/*" { capabilities = ["list", "delete"] } path "transit_cv3/*" { capabilities = ["create", "update", "read", "delete", "list"] }The policy should be stored with a name. For example,
cv3_policy.Enable AppRole authentication. This can be done with command line:
# Enable approle auth method vault auth enable approle # Create the role for cv3 vault write auth/approle/role/cv3_role \ secret_id_ttl=10m \ token_num_uses=10 \ token_ttl=20m \ token_max_ttl=30m \ secret_id_num_uses=40 \ token_policies="cv3_policy" # Get the role ID vault read auth/approle/role/cv3_role/role-id # Get the secret ID vault write -f auth/approle/role/cv3_role/secret-id
The role ID is unique to each role and remains unchanged, even if the AppRole configuration is updated. In contrast, the secret ID is regenerated each time it is requested, and any previously issued secret ID becomes invalid.
In the example above, the secret ID is valid for 10 minutes after creation and can be used up to 40 times. Regardless of the authentication method (AppRole, OIDC, etc.), the client ultimately receives a token for the session. This token is configured to expire after 20 minutes and can be renewed up to a total of 30 minutes. It may be used a maximum of 10 times.